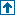



Describes all steps of behavior recognition; example for facial expressions.
The file describes the following:
1) data format [3 choices]
2) feature detection & description [2 choices]
3) behavior classification
Data and additional information can be obtained at:
http://vision.ucsd.edu/~pdollar/research/research.html
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DATA FORMAT
First the directory of the data must be specified.
Alter datadir.m to point to the location of the data.
Behavior data can be represented in 1 of 3 ways. In each case data is divided into a
number of 'sets', each set contains data that should be treated together (for training
and testing, see generating results for more info). In each case, a set contains a
number of behavior clips. The three methods for representing a set are:
[set_ind] the 2 digit set index, '00','01',...
[cliptype] represents behavior type, such as 'grooming' or 'smiling'
[instance] represents the 3 digit instance number - '000','001',...
1) .avi files in a datadir/set[set_ind]/, named '[cliptype][instance].avi'
2) .mat files in a datadir/set[set_ind]/, named 'clip_[cliptype][instance].mat'
When loaded the file contains two matlab variables: 'I' and 'clipname'
3) a single DATASETS struct, kept in memory as DATASETS, described below.
If all the sets can be stored in memory at once, the third option can be used. DATASETS
is an array of nsets elements, where each element is a struct representing a set of
data. Each DATASETS should initally have the following two fields: IS and IDX. IS is
either a ...xN 4D array of N clips or an N element cell array of clips (3D arrays). IDX
should be a length N uint8 vector of clip types. Note that as processing proceeds the
contents of DATASETS will change.
One can convert between the formats using the conv_* functions. To go from DATASETS
format to .avi format, go through the .mat format.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FEATURE DETECTION & DESCRIPTION
These functions are used to detect cuboids and than apply descriptors to them, creating
data that can than be used in various training / testing scenarios described next. The
two function featuresSM and featuresLG both return the same output. The difference is
that featuresSM works with data fully in memory (the DATASETS format), while featuresLG
writes things back and forth to the hard disk (using the .mat format). If the files are
originally in .avi format, they need to be converted to either .mat format or the
DATASETS format.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BEHAVIOR CLASSIFICATION
See recog_test or recog_test_nfold
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EXAMPLE below